Data Cleaning
If You do not clean the data before training or testing Your Model then if your data is not good enough to apply machine learning algorithms then you would get trivial results like famous saying “Garbage In, Garbage Out.”
suppose you have data something like this
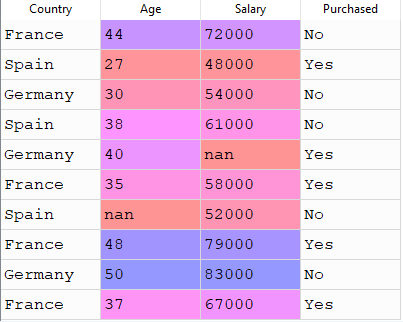
if you look closely into this dataset then you would find some “nan” values into age and salary column.what the meaning of nan ?
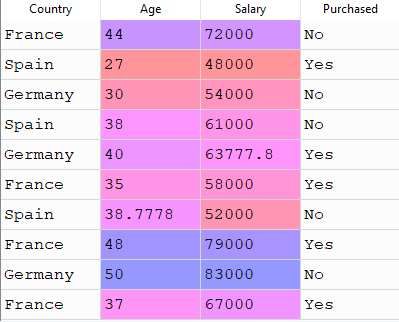
nan means absense of value.You have two options either you could fill some data into this ‘nan’ cell or you could remove that row.
if you want to fill data into that cell then what would be that data ? we generally fill this data with mean of that columns value
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv('Data.csv') # load data
X = data.iloc[:,0:3] # take all rows and col [0,3-1]
Y = data.iloc[:,3] # take 4th col
from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer
imputer = Imputer(missing_values=np.nan,strategy="mean",axis=0) # replace missing values with mean
X[:,1:3] = imputer.fit_transform(X[:,1:3]) # since only 2nd and 4th column contains nan
after executing above code X would look like this
if You know about gradient descent then you probably woundering how you could fit this data because in our cost function we do not use any string values we only use numbers.
since our algorithm can understand only numbers so we should change the labels into numbers using LabelEncoder. These labeled feature is also called as categorical feature.
LabelEncoder takes every unique label and give that lable to one value for example if we have three labels A,B,C then LabelEncoder would represent A,B,C by 1,2,3 respectively.
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
labelencoder = LabelEncoder()
X[:,0] = labelencoder.fit_transform(X[:,0])
Y = labelencoder.fit_transform(Y)
now you should come up with this question how did you assigned arbitrary values to labels ? wouldn't our model be biased towards minimum or maximum valued label? Yes it would be biased that's why we will have to do one more step.
we will use one-hot encoding to resolve above problem. If we have 'n' labels then we take n dimensional vector to represent each label and for each label one cell is dedicated. and if we have to represent a label then only the cell which is dedicated for this label will have value 1 and rest cells values will be zero. for example if we have three levels A,B,C then we would represent A,B,C using 3 dimensional vector suppose 1st,2nd and 3rd cells are dedicated for A,B and C respectively.then
A = [1,0,0]
B = [0,1,0]
C = [0,0,1]
now X would look like this

let's look at the code
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
onehotencoder = OneHotEncoder(categorical_features=[0]) # select categorical features columns
X = onehotencoder.fit_transform(X).toarray()
Now one last step we would do for reduce biasing. what if one feature value is much larger than other features so that our model is biased towards that feature ? to resolve this biasing and Converge Gradient Descent fast we do feature scaling . In feature scaling we bring all features into same range using some standard methods. for example if we use min-max scaling then use following formula
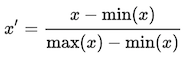
first we find maximum and minimum element in a column and we call it ‘max(x)’ and ‘min(x)’ for that column and for each element ‘x’ we iterate through whole column using above formula.
we will use sklearn’s StandardScaler to implement this . there are various methods of feature scaling you could use whatever method gives best result for your problem.
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
standardscaler = StandardScaler()
X = standardscaler.fit_transform(x)
Finally X would look like this
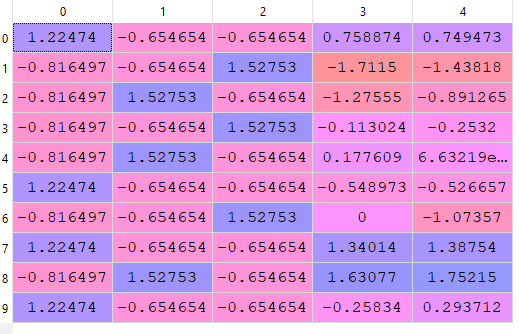
Look at the values of X all features are almost in the same range.
